全てのコントーロルがコマンドを持つわけではないので、イベントからコマンドに変換してとバインドする方法を試してみます。
サンプルコード
・プロジェクトの作成
dotnet new wpf -f net8.0 -n NoXAML04
cd NoXAML04
rm *.xaml
rm MainWindow.xaml.csファイル名:NoXAML04.csproj
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<OutputType>WinExe</OutputType>
<TargetFramework>net8.0-windows</TargetFramework>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
<UseWPF>true</UseWPF>
<StartupObject>NoXAML04.App</StartupObject>
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>
ファイル名:RelayCommand.cs
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace NoXAML04;
public class RelayCommand : ICommand
{
private readonly Action<object?> _execute;
private readonly Func<object?, bool>? _canExecute;
public RelayCommand(Action<object?> execute, Func<object?, bool>? canExecute = null)
{
_execute = execute;
_canExecute = canExecute;
}
public bool CanExecute(object? parameter) => _canExecute?.Invoke(parameter) ?? true;
public void Execute(object? parameter) => _execute(parameter);
public event EventHandler? CanExecuteChanged;
public void RaiseCanExecuteChanged() => CanExecuteChanged?.Invoke(this, EventArgs.Empty);
}ファイル名:EventBindingHelper.cs
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace NoXAML04;
public static class EventBindingHelper
{
public static void BindEventToCommand(UIElement element, string eventName, ICommand command, object? commandParameter = null)
{
var eventInfo = element.GetType().GetEvent(eventName);
if (eventInfo == null)
throw new ArgumentException($"イベント {eventName} が {element.GetType().Name} に見つかりません");
// イベントハンドラを生成
var handler = new RoutedEventHandler((s, e) =>
{
if (command.CanExecute(commandParameter))
{
command.Execute(commandParameter);
}
});
// イベントに追加(Button.Click のようなイベントに対応)
eventInfo.AddEventHandler(element, handler);
}
}ファイル名:MainWindowViewModel.cs
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace NoXAML04;
public class MainWindowViewModel
{
public ICommand ClickCommand { get; }
public MainWindowViewModel()
{
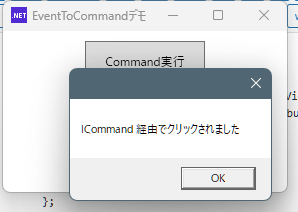
ClickCommand = new RelayCommand(_ => MessageBox.Show("ICommand 経由でクリックされました"));
}
}
ファイル名:App.xaml.cs
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
namespace NoXAML04;
public class App : Application
{
// エントリポイント
[STAThread]
public static void Main()
{
var app = new App();
app.Startup += (sender, e) =>
{
var viewModel = new MainWindowViewModel();
// UIの構築
var button = new Button
{
Content = "Command実行",
Width = 120,
Height = 40,
Margin = new Thickness(10)
};
// EventToCommand的にバインド:Click → ViewModelのCommand
EventBindingHelper.BindEventToCommand(button, "Click", viewModel.ClickCommand);
var stackPanel = new StackPanel
{
Children = { button }
};
// ウィンドウの構築と表示
var window = new Window
{
Title = "EventToCommandデモ",
Width = 300,
Height = 200,
DataContext = viewModel,
Content = stackPanel,
};
window.Show();
};
app.Run();
}}実行イメージ
1.ボタンをクリック
2.メッセージボックスが表示されます。
解説
BindEventToCommand()でbuttonオブジェクトを引数に”click”イベントに対しビューモデルのコマンドと関連付けを行っています。
この方法ですと、コントロールのオブジェクトとイベントの名称を知っていれば、コマンドと紐づけることが出来るので、コントロール側にコマンドプロパティが無い要素でもコマンドを実行することが出来ます。
今回のサンプルでは Click イベントを扱っているため、RoutedEventHandler 型で問題なく動作しますが、実際にはコントロールとイベント名の組み合わせによって、イベントの型(EventArgsの種類)も異なるため、コード側で分岐する必要があります。
以下はその一例です:
if (element is Image && eventName == "MouseDown")
{
element.MouseDown += (s, e) =>
{
if (command.CanExecute(e)) command.Execute(e);
};
}
else if (element is TextBox && eventName == "KeyDown")
{
element.KeyDown += (s, e) =>
{
if (command.CanExecute(e)) command.Execute(e);
};
}
このように、イベントの種類ごとに EventArgs の型が異なるため、個別にハンドラを用意する必要があり、数が増えると管理が煩雑になります。
そのため、最終的には EventToReactiveCommand() など、既存のライブラリの力を借りる方が、実用的かつ保守性の高い選択と言えるでしょう。
追記:20250711
頑張ってEventToReactiveCommand()を作りましたが、イベントからViewModelのICommandを呼び出しても良いのかもしれない。
例
// ビューパネルドロップイベント
_viewPanel.Drop += (sender, e) =>
{
if (viewModel.DropCommand.CanExecute())
{
viewModel.DropCommand.Execute(e);
};
};NoXAMLだとMVVMでも、コードビハインドを使うことに、ためらいが少なくなる点が良いと思います。


コメント