C#でビットマップオブジェクトと言うとSystem.Drawing.Bitmapを思い浮かべる方も多いでしょう。しかしながら、この記事で扱うビットマップオブジェクトは、System.Windows.Media.Imaging.BitmapSourceで、主にWPFで扱われるビットマップオブジェクトに成ります。System.Drawing.Bitmapと異なる点として、Freeze()で異なるスレッド間で安全にオブジェクトを受け渡しが出来る、スレッドセーフである点。またIDisposableでは無いのでusingやDispose()が不要である点があげられます。
基本的なこと
WPFで扱うオブジェクトですので、Consoleプロジェクトで扱う場合プロジェクトファイルを以下の様に変更します。
<UseWPF>true</UseWPF> <!-- 追記 -->
<TargetFramework>net8.0-windows</TargetFramework> <!-- 変更 -->net8.0を想定していますが数値はフレームワークのバージョンに合わせる。
また、static void Main()の前に[STAThread]を記述する必要があります。
BitmapSourceはWPFで扱うビットマップオブジェクトのベースクラスで、実際ビットマップオブジェクトを扱う場合は派生クラスを扱うことに成ります。
主な派生クラスの例:
- BitmapImage … 画像ファイルなどから生成しやすいビットマップオブジェクト
- WriteableBitmap … 書き換え可能なビットマップオブジェクト
多くの派生クラスが存在しますが、その総称としてBitmapSourceがつかえます。具体的にはメソッドの引数や、戻り値にBitmapSourceを指定すると、様々な派生クラスのオブジェクトに対応出来て便利です。
画像ファイル(Stream)から生成
BitmapImageをファイルから生成する
画像ファイルを読み込んでBitmapImageを生成します。
// 画像ファイルから生成する。
public static BitmapImage Load(string imageFile)
{
using var stream = new FileStream(imageFile, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
return Load(stream);
}
// Streamから生成する。
public static BitmapImage Load(Stream stream)
{
BitmapImage bitmap = new();
bitmap.BeginInit();
bitmap.CacheOption = BitmapCacheOption.OnLoad;
bitmap.StreamSource = stream;
bitmap.EndInit();
bitmap.Freeze();
return bitmap;
}
以下のusingが必要になります。
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows;
using System.IO;ファイルの読み込みとデコードを別処理にすることを想定して、引数がStreamのメソッドを用意しました。
WritableBitmapへ変換
// BitmapSourceをWritableBitmapへ変換
public static WriteableBitmap Convert(BitmapSource source)
{
// ピクセルフォーマットとサイズ情報を取得
int width = source.PixelWidth;
int height = source.PixelHeight;
double dpiX = source.DpiX;
double dpiY = source.DpiY;
PixelFormat format = source.Format;
BitmapPalette? palette = source.Palette;
// 1行のバイト数(stride)を計算
int bytesPerPixel = (format.BitsPerPixel + 7) / 8;
int stride = width * bytesPerPixel;
byte[] pixels = new byte[stride * height];
// BitmapSource からピクセルデータをコピー
source.CopyPixels(pixels, stride, 0);
// WriteableBitmap を生成し、ピクセルを書き込み
var writeable = new WriteableBitmap(width, height, dpiX, dpiY, format, palette);
writeable.WritePixels(new Int32Rect(0, 0, width, height), pixels, stride, 0);
return writeable;
}
なお、WriteableBitmap は BitmapSource の派生クラスであるため、逆方向の変換は不要で、そのまま BitmapSource として扱うことができます。
DPIとピクセルフォーマット変換
画像ファイルは様々なDPIやピクセルフォーマットが存在しますが、アプリで扱う場合非常に面倒です。
以下の変換コードを使いDPIを96、ピクセルフォーマットをBGRAに変換します。
// DPIとピクセルフォーマットを変換
public static BitmapSource ConvertToDPI96BGRA(BitmapSource source)
{
const double targetDpi = 96.0;
var format = PixelFormats.Bgra32;
// フォーマット変換が不要ならスキップ
bool formatMatch = source.Format == format;
bool dpiMatch = source.DpiX == targetDpi && source.DpiY == targetDpi;
// 両方一致していれば変換不要
if (formatMatch && dpiMatch)
{
return source;
}
// フォーマット変換(必要なら)
BitmapSource converted = formatMatch
? source
: new FormatConvertedBitmap(source, format, null, 0);
// DPI変換(常に BitmapSource.Create)
int width = converted.PixelWidth;
int height = converted.PixelHeight;
int bytesPerPixel = (format.BitsPerPixel + 7) / 8;
int stride = width * bytesPerPixel;
byte[] pixels = new byte[stride * height];
converted.CopyPixels(pixels, stride, 0);
var result = BitmapSource.Create(
width, height,
targetDpi, targetDpi,
format,
null,
pixels,
stride);
result.Freeze();
return result;
}
DPIやピクセルフォーマットを決め打ちするのも如何なものかと思いますが、後続の処理がシンプルになり、不具合を避けられます。
PNG形式で保存
// PNG形式で保存
public static void SaveAsPng(BitmapSource bitmap, string filePath)
{
var encoder = new PngBitmapEncoder();
encoder.Frames.Add(BitmapFrame.Create(bitmap));
using var stream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
encoder.Save(stream);
}
残念なおしらせ
PNGファイルの圧縮レベルを指定することは出来ません。
内部的に高圧縮が指定されているらしく、出来上がるファイルサイズはそこそこ小さくなりますがエンコード(圧縮)が遅いのが難点です。
独自画像フォーマットによる保存と読み込み
世の中には無数の画像フォーマットがあるのに、独自フォーマットを作る理由を説明します。
「画像フォーマットという物を一度作ってみたかった」という個人的な欲求満たすために作られました。
それだとあんまりなので、それらしい理由を述べますと、
エンコード、デコードに要する時間が極小で、可逆で劣化せず、アルファチャンネルが記録できるフォーマットが見つけられませんでした。BMP形式はアルファチャンネルが保持できず、PNGはエンコード・デコードが重いという理由から作りました。ただ、このままだとファイルサイズが大きくなりすぎなので、実用的にはLZ4などの軽量な圧縮を行うことになると思います。
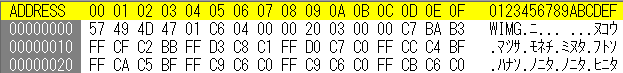
ヘッダ構造:
[Magic:4] [Format:1] [Width:4] [Height:4] [PixelData...]- Magic: “WIMG”
- Format: 0x01 = 非圧縮、0x02 = LZ4(将来拡張用)
- Width, Height: 各4バイトの整数(Int32)
- PixelData: BGRA形式(非圧縮)
保存メソッド
// 独自画像フォーマットWINGで保存
public static void SaveWimg(BitmapSource bitmap, string filePath)
{
const string magic = "WIMG";
const byte format = 0x01; // 非圧縮
int width = bitmap.PixelWidth;
int height = bitmap.PixelHeight;
int bytesPerPixel = (bitmap.Format.BitsPerPixel + 7) / 8;
int stride = width * bytesPerPixel;
byte[] pixels = new byte[stride * height];
bitmap.CopyPixels(pixels, stride, 0);
using var stream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
using var writer = new BinaryWriter(stream);
writer.Write(System.Text.Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(magic));
writer.Write(format);
writer.Write(width);
writer.Write(height);
writer.Write(pixels);
}
読み込みメソッド
// 独自画像フォーマットWINGで読み込み
public static WriteableBitmap LoadWimg(string filePath)
{
const string expectedMagic = "WIMG";
using var stream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
using var reader = new BinaryReader(stream);
var magic = System.Text.Encoding.ASCII.GetString(reader.ReadBytes(4));
if (magic != expectedMagic)
throw new InvalidDataException("ファイル形式が不正です(識別子が一致しません)");
byte format = reader.ReadByte();
if (format != 0x01)
throw new NotSupportedException("この形式の読み込みには未対応です");
int width = reader.ReadInt32();
int height = reader.ReadInt32();
var pixelFormat = PixelFormats.Bgra32;
int bytesPerPixel = (pixelFormat.BitsPerPixel + 7) / 8;
int stride = width * bytesPerPixel;
byte[] pixels = reader.ReadBytes(stride * height);
var bitmap = new WriteableBitmap(width, height, 96, 96, pixelFormat, null);
bitmap.WritePixels(new Int32Rect(0, 0, width, height), pixels, stride, 0);
return bitmap;
}


コメント