データをバインディングをする場合バインディングソースとなるオブジェクトはINotifyPropertyChangedの実装である必要があります。
また、コマンドをバインディングする場合、ICommandを実装する必要となります。
この記事ではINotifyPropertyChangedとICommandを実装したサンプルコードを解説することで、バインディングの概要を確認します。
サンプルコード
ファイル名:binding1.csproj
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<OutputType>WinExe</OutputType>
<TargetFramework>net8.0-windows</TargetFramework>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
<UseWPF>true</UseWPF>
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>
ファイル名:ActionCommand.cs
using System;
using System.Windows.Input;
public class ActionCommand : ICommand
{
private readonly Action<object?> _execute;
private readonly Predicate<object?> _canExecute;
public ActionCommand(Action<object?> execute, Predicate<object?> canExecute)
{
_execute = execute;
_canExecute = canExecute;
}
public bool CanExecute(object? parameter)
=> _canExecute(parameter);
public void Execute(object? parameter)
=> _execute(parameter);
public event EventHandler? CanExecuteChanged;
public void RaiseCanExecuteChanged()
=> CanExecuteChanged?.Invoke(this, EventArgs.Empty);
}
ファイル名:MainViewModel.cs
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
namespace binding1;
public class MainViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private string? _selectedValue;
public string? SelectedValue
{
get => _selectedValue;
set
{
if (_selectedValue == value) return;
_selectedValue = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
// ★ parameter の元が変わったので通知
ActionCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
}
}
public ActionCommand ActionCommand { get; }
public MainViewModel()
{
ActionCommand = new ActionCommand(
execute: p =>
{
var value = (string)p!;
// 実行処理
if (value is not null)
{
Debug.Print($"{value}");
}
},
canExecute: p =>
{
return !string.IsNullOrEmpty(p as string);
}
);
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler? PropertyChanged;
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string? name = null)
=> PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(name));
}
ファイル名:MainWindow.xaml.cs
using System.Windows;
namespace binding1;
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
}
ファイル名:MainWindow.xaml
<Window x:Class="binding1.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:binding1"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="binding1" Height="150" Width="300">
<Window.DataContext>
<local:MainViewModel />
</Window.DataContext>
<StackPanel Margin="20">
<!-- parameter の元 -->
<TextBox Text="{Binding SelectedValue, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" />
<!-- parameter が Command に流れる -->
<Button Content="Execute"
Margin="0,10,0,0"
Command="{Binding ActionCommand}"
CommandParameter="{Binding SelectedValue}" />
</StackPanel>
</Window>
サンプルコードの仕様
起動時、テキストボックスは空の状態で、ボタンは非活性(押せない)状態です。
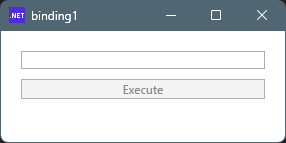
テキストボックスに文字を入力すると、ボタンが活性化され押せる状態になります。
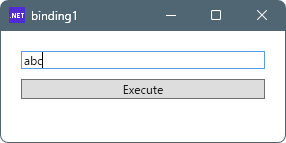
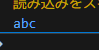
ボタンを押すとテキストボックスの内容が出力されます。
解説
MainWindow.xaml
Viewに相当し、UIのデザインを静的に宣言しています。
・MainWindow.xamlのデータソースをMainViewModelに設定する。
<Window.DataContext>
<local:MainViewModel />
</Window.DataContext>・テキストボックスの定義
<TextBox Text="{Binding SelectedValue, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" />
MainViewModelクラスのSelectedValueプロパティとバインディングすることを宣言しています。
UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChangedを指定することで、1文字入力することに変更イベントもとに、内容の変更バインディング(同期処理)が実行されます。
指定しない場合、TextBoxからフォーカスが失われた際、バインディングされます。
・ボタンの定義
<Button Content="Execute"
Margin="0,10,0,0"
Command="{Binding ActionCommand}"
CommandParameter="{Binding SelectedValue}" />CommandプロパティがActionCommandプロパティとバインディングすることを宣言しています。
また、CommandParameterはSelectedValueとバインディングすることを宣言しています。
SelectedValueは、TextBoxのText(入力値)ともバインドしていますので、TextBoxの入力した内容が、CommandParameterに影響を与えます。
ActionCommand.cs
ICommandの実装です。
コンストラクタで、実行するコードを
Action<object?> executeで、コマンドが有効・無効のフラグを
Predicate<object?> canExecuteで、引数として渡されて、メンバーとしてセットされます。
そして、
public void Execute(object? parameter)や
public bool CanExecute(object? parameter)で、実行されます。
public void RaiseCanExecuteChanged()では、
CanExecuteChanged?.Invoke(this, EventArgs.Empty);で、イベントを発火しています。
こちらは、parameter(CommandParameter)であるSelectedValueが変更された際、呼び出されるようにすることで、
CanExecuteが変化した可能性があることを通知しています。
MainViewModel.cs
まず、
public ActionCommand ActionCommand { get; }は、前項のActionCommandをプロパティとして公開しています。
またコンストラクタ内で、
ActionCommand = new ActionCommand(
execute: p =>
{
var value = (string)p!;
// 実行処理
if (value is not null)
{
Debug.Print($"{value}");
}
},
canExecute: p =>
{
return !string.IsNullOrEmpty(p as string);
}
);ActionCommandを生成し、
executeでコマンドで実行したい内容(入力文字のデバック出力)と、
canExecuteで実行の許可フラグ(入力文字がnull又は空ではないこと)
を定義しています。
private string? _selectedValue;
public string? SelectedValue
{
get => _selectedValue;
set
{
if (_selectedValue == value) return;
_selectedValue = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
// ★ parameter の元が変わったので通知
ActionCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
}
}SelectedValueプロパティをプロパティと公開し、バインドソースとして機能します。
getはメンバー変数_selectedValueをそのまま返します。
setは、_selectedValueにvalueをセットするわけですが、
セットされるということは値が変更されることに成りますので、
OnPropertyChanged();で、変更を通知しています。
OnPropertyChangedのCallerMemberNameは、nameがnullの場合(引数を省略)プロパティの名前(この場合”SelectedValue”)がセットされます。
また、
ActionCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();で、ActionCommandにも、SelectedValueが変化したことを通知し、
ボタンの実行可能・不可能フラグにに連動(バインディング)します。
流れ
各コードは最終的に
CanExecuteChanged
と
PropertyChanged
にたどり着きますが、
これ以降のコードは記述されていません。
それは、
バインディングシステム側で、
処理されているためと考えられます。
① データの流れ
② 通知の流れ
汎用ベースクラス
INotifyPropertyChangedやICommandの実装は、
毎回同じようなコードになるので、
ベースクラスにまとめて継承する使い方が便利です。
ViewModelのベースクラス
ViewModelBase.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
public abstract class ViewModelBase : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler? PropertyChanged;
protected virtual void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string? propertyName = null)
=> PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
/// <summary>
/// backing field を更新して PropertyChanged を発火する定番ヘルパー。
/// </summary>
protected bool SetProperty<T>(
ref T field,
T value,
Action? onChanged,
[CallerMemberName] string? propertyName = null)
{
if (EqualityComparer<T>.Default.Equals(field, value))
return false;
field = value;
onChanged?.Invoke();
OnPropertyChanged(propertyName);
return true;
}
}
/*
使い方1
public sealed class MainViewModel : ViewModelBase
{
private string? _name;
public string? Name
{
get => _name;
set => SetProperty(ref _name, value);
}
}
使い方2
private string? _firstName;
private string? _lastName;
public string? FirstName
{
get => _firstName;
set => SetProperty(ref _firstName, value, () => OnPropertyChanged(nameof(FullName)));
}
public string? LastName
{
get => _lastName;
set => SetProperty(ref _lastName, value, () => OnPropertyChanged(nameof(FullName)));
}
public string FullName => $"{FirstName} {LastName}".Trim();
*/Commandのベースクラス
RelayCommand.cs
public sealed class RelayCommand<T> : ICommand
{
private readonly Action<T?> _execute;
private readonly Func<T?, bool>? _canExecute;
public RelayCommand(Action<T?> execute, Func<T?, bool>? canExecute = null)
{
_execute = execute ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(execute));
_canExecute = canExecute;
}
public bool CanExecute(object? parameter)
=> _canExecute?.Invoke((T?)parameter) ?? true;
public void Execute(object? parameter)
=> _execute((T?)parameter);
public event EventHandler? CanExecuteChanged;
public void RaiseCanExecuteChanged()
=> CanExecuteChanged?.Invoke(this, EventArgs.Empty);
}
/*
使い方(ViewModelBaseと一緒に使う例)
public sealed class MainViewModel : ViewModelBase
{
private string? _text;
public string? Text
{
get => _text;
set
{
if (SetProperty(ref _text, value))
{
SaveCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
}
}
}
public RelayCommand SaveCommand { get; }
public MainViewModel()
{
SaveCommand = new RelayCommand(
execute: Save,
canExecute: () => !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(Text)
);
}
private void Save()
{
// 保存処理
}
}
*/


コメント